 Among all the attributes of the greatest leaders of our time, one stands above the rest: They are all highly trusted. You can have a compelling vision, rock-solid strategy, excellent communication skills, innovative insight, and a skilled team, but if people don’t trust you, you will never get the results you want. David Horsager
Among all the attributes of the greatest leaders of our time, one stands above the rest: They are all highly trusted. You can have a compelling vision, rock-solid strategy, excellent communication skills, innovative insight, and a skilled team, but if people don’t trust you, you will never get the results you want. David Horsager
Here are some characteristics of trust.
Trust is earned; you can’t buy it or obtain it through coercion.
It takes time for trust to develop and it doesn’t come quickly. When you assume a new position of leadership, your good reputation of being trustworthy may help jumpstart the trust factor with your new team members but inevitably they will need to see you in action and to experience, firsthand, your trustworthiness; and that takes time.
Trust is built and maintained by hundreds of small and large actions over time.
Every decision you make and every action you take either adds to or subtracts from your “trust account.”
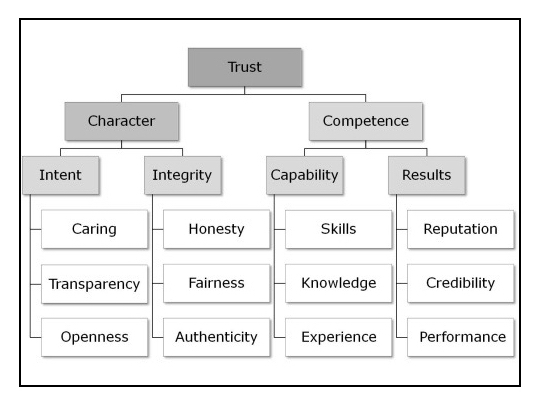
In leadership, trust is built on two pillars: character and competence.
To be a trustworthy individual, only one is needed: character; but to be a trustworthy leader, you must exhibit both character and competence.
Character includes two areas and six attributes:
Your intentions must be:
- Caring – people don’t care how much you know until they know how much you care
- Transparent – don’t have hidden agendas or motivations
- Open – don’t withhold critical information
Your integrity is demonstrated through:
- Honesty – be truthful and straightforward; don’t lie, cheat, or steal
- Fairness – being fair is not treating everyone the same, but treating each individual as he deserves
- Authenticity – Luther Price succinctly said, “Be what you is, not what you ain’t; ’cause if you ain’t what you is, you is what you ain’t.”
Competence includes two areas and six traits:
You must demonstrate capability through:
- Skills – do you have the necessary skills for your trade?
- Knowledge – do you understand the basic principles of what makes your organization work?
- Experience – is your knowledge only theoretical or has it been proven experientially?
People will trust your results because of your:
- Reputation – the sum of all your work and leadership experience.
- Credibility – reliability; your ability to produce over time.
- Performance – do you consistently prove your ability to “Get ‘er done.”
Trust alone won’t make you a great leader, but without trust you will never be one.
[reminder]What are your thoughts about this essay?[/reminder]
[callout]Click here for information about the September 27-28 Lead Well workshop.[/callout]
 Imagine that you’re in a dark auditorium and suddenly a spotlight is turned on. It is bright and clearly illumines the area it shines on. But it is a limited area and someone is controlling where you are looking.
Imagine that you’re in a dark auditorium and suddenly a spotlight is turned on. It is bright and clearly illumines the area it shines on. But it is a limited area and someone is controlling where you are looking. Have you ever wondered why negative events seem to impact us more than positive events?
Have you ever wondered why negative events seem to impact us more than positive events? I enjoy cruising because it’s a win-win situation; it works for me and it works for the cruise line. I recently paid only $1,350 for a luxurious, 16-day transatlantic/European cruise (Miami to Rome) which included all meals, lodging, transportation, and entertainment. One evening, as I was munching on a filet mignon, I wondered, “How do they make this work, financially?” I don’t know, but obviously they do, or they wouldn’t be in business.
I enjoy cruising because it’s a win-win situation; it works for me and it works for the cruise line. I recently paid only $1,350 for a luxurious, 16-day transatlantic/European cruise (Miami to Rome) which included all meals, lodging, transportation, and entertainment. One evening, as I was munching on a filet mignon, I wondered, “How do they make this work, financially?” I don’t know, but obviously they do, or they wouldn’t be in business.